

Driving force for WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) management has never been more important than it is today in order to save global resources and to reach the bold goal in EU for circular economy (European Green Deal). Recycling is seen as real business not only in companies focusing on recycling and material management, but also in companies that sell consumer electronics.
This paper describes a project, which developed a concept for an IoT solution to support recycling of electronic equipment. The project was a part of CEDIM (Circular Economy Digital Marketplace) project funded by Helsinki- Uusimaa Regional Council to develop a digital marketplace for WEEE in Finland.
The goal for this project was to develop and implement a prototype of a system used to receive electrical equipment for recycling in circular economy entry point. Developed solution is based on combination of RFID technology and computer vision to provide automated identification and assessment of condition of the equipment and registration of the equipment to a digital market place. The entry points operate as MQTT brokers, which publish the information to digital market place. MQTT was chosen due it is lightweight protocol optimizing also the use of resources in communication. At this phase, the focus of the project is in ICT equipment and public schools in Finland.
==> Abstract (PDF)By default, we assume an HTTPS connection being marked as valid and highlighted in green by a browser should be secure. Nevertheless, it highly depends on the actual implementation of an app and if it is hardened against interception attacks. While it is always possible to use reengineering techniques to circumvent protections, an even more amazing way would be to do exactly that without modifying apps.
This talk will guide you through a possible way to solve that challenge and to intercept communication, while most apps are not aware of it.
Nowadays, Information Technology (IT) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are widely exploited to industry, to automate manufacturing and increase productivity. However, this automated industrial environment assumes that the personnel is capable to identify potential cybersecurity threats and able to respond adequately when an attack is identified. Nevertheless, there is a lack of well-trained technicians and industries can hardly find qualified personnel. The Digital Training for Cybersecurity Students in Industrial Fields (DICYSTECH)- is a two-year EU funded project that aims to fill the gap and provide industry the necessary open-source tools to train their personnel.
The DICYSTECH project, unites five EU partners from Greece, Portugal, Italy and Spain in the development of open access cybersecurity training modules and linked cybersecurity remote laboratories for cybersecurity education. DICYSTECH will create 5 innovative digital DICYSTECH Modules in both technical and transversal competences for cybersecurity students in Industrial environments available via an open attractive e-learning platform, and three fully developed remote cybersecurity laboratories in which learners can view and experiment with high end enabling IT technology and cybersecurity measures in simulated industrial contexts. The Modules will cover Industrial Networks, Equipment and Network Protection (deploying and maintaining cybersecurity in advanced industrial contexts), the Forensic (security) Analysis of these networks and countermeasures to threats, and transversal competences necessary for cybersecurity technicians. Each Module will offer learning challenges and digital tests to support learning upon completion of the learning activities. The Project will also develop a DICYSTECH HUB that will coordinate access to the three remote labs, and also serve as an authentication and booking system.
==> Abstract (PDF)According to the World Health Organization up to 5 out of every 1000 children are born deaf or hard of hearing. Οbviously, these children must be educated by teachers adequately trained in Sign Languages, the native languages of the Deaf, so that they are able to communicate and to develop linguistically. However, it is hard for Higher Education Institutes – and other education levels as well- to find and employ as tutors experts in Sign Language.
Computer Assisted Teaching in Sign Language (CAT-SL) is a three-year EU funded project that aims to fulfill this gap and develop an innovative and affordable system for interactive SL teaching for students in Special Education/Pedagogical departments and primary school education. CAT-SL project will develop a curricula and guides for teaching SL using the CAT-SL system for at least two multilingual courses, in partners countries - Greece, Cyprus, Portugal and Netherlands- to support the social inclusion of the deaf children. The CAT-SL system is based on computer-vision, machine-learning, linguistic technology, and avatars developed by all the involved partners in several ongoing or recently completed national and EU-funded projects.
The project differentiates from other similar efforts for SL analysis and systems due to the the adoption of a more global approach, necessary to create a system that could be extended to more international Sign Languages.
==> Abstract (PDF)Getting experienced with electronics and embedded systems is a challenging task for teaching staff when they have to deal with students without prior knowledge. The shorter the program, the harder it is to give students insight in the aspects of the technology behind our digitized world. The associate degree IoT, a two year program, started two years ago. An embedded platform which is a compromise between the in depth knowledge and the complexity of the embedded world is the Atmega Xplained Mini.
While only KNX was a domotica course in our programs in the past, smart home solutions made there entrance in our projects. One of these platforms is a Home Assistant. This presentation gives a brief overview if one starts with Home Assistant.
In this paper the Erasmus+ ACTEA project is presented, with its goals, ambitions and results.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the science that make computers capable of imitating human intelligence such as decision making, text processing, and visual perception. It builds machines, which learn from experience and adjust their inputs to perform human specific tasks accordingly.
The computers are trained through processing large volume of data to simulate the logic in them. Nowadays, AI has become more popular since it automates repetitive learning and analyses the data deeper and discovers the patterns with incredible accuracy. AI is a broader field that contains several subfields such as machine learning, robotics, and computer vision.
Machine learning (ML) is a subfield of artificial intelligence which focuses on the use of data and algorithms to imitate the way that human learns and enables a computer to learn without explicit programming. To predict output values within a satisfactory range, machine learning uses designed algorithms to obtain and interpret input data through the use of statistical methods. They learn and optimise their operations as new data is fed into these algorithms to enhance performance and develop intelligence over time.
In this paper we will have a closer look at concepts of machine learning and some tools used to implement them.
==> Abstract (PDF)Virtual Reality (VR) is an effective medium for developing and practicing skills. Combined with instructional design, it can potentially have a more significant effect on learning efficiency, learning curve, and retention than classical lectures or instruction videos. As a result, the amount of VR training has exploded. Building convincing and interactive VR training experiences is expensive. Even after considerable investment, the result is a static learning experience that does not adjust to the user’s needs and skill set and offers a small number of training scenarios with no variations to improve replay value.
Therefore, we propose a programming model & architecture for adaptive VR training experiences. From a deployment standpoint, it works by launching VR training experiences from training configuration files. These files describe training scenarios from a well-defined semantic structure. Such an architecture essentially decouples the problem of generating training scenarios, which developers can do without game development experience, from the challenge of creating real-time, immersive VR experiences. End users can generate the training configuration files through a user-friendly training scenario editor. Software developers can also use Artificial Intelligence algorithms to procedurally generate new training scenarios which adapt automatically to the user’s skill set.
Our programming model generalizes well to novel VR training types and has been applied successfully to fire training, evacuation training, and the manipulation of industrial machinery.
Blended Mobility Project methodology is devoted to create and manage international multidisciplinary teams of students who will collaborate in order to develop a solution for an engineering problem. These teams are set up for a semester with the purpose of developing and presenting a prototype or a proof of concept for a given challenge.
Blended Mobility Project in the academic year 2021/22, completed its 12th edition which started in the academic year 2009/10. Altogether HIEs from 11 countries were participating including Portugal, Belgium, Germany, the UK, Greece, Italy, Kurdistan - Iraq, Slovenia, Nigeria, France and Lithuania. Information Technology companies provide real project proposals. With this professional involvement, students got a context which is international, multicultural, multidisciplinary and professional.
The preparation of the course starts at the beginning of the first semester in October. At this stage the teachers collect challenges from companies and select the most interesting with regards to its pedagogical potential. Initially 13 projects were selected. The selected challenges are presented to final-year-undergraduate or master students. Each project is implemented by a team of about 10 students which are mainly from Information Technology and Software Engineering disciplines but students from other fields of study, such as: Business Development, Management, Electronics, IT & Design participate. Applicants are selected based on a set of criteria defined by each partner university and the teams for each challenge are setup. In 2021/22 edition, more than 53 students were involved actively, as well as 14 teachers from the 11 participating HEIs. Allocating 7-9 students per team the most 7 popular projects among the students were chosen to be implemented. This process was concluded by the end of January and the first face-to-face meeting that runs at the beginning of the second semester, took place at Ghent, Belgium, 21-25 February, 2022. At this first face-to-face meeting, students get to know each other, the company offering the challenge and its details. The challenge is provided to the students by the company but no specifications are given concerning the solution to develop; that is the students task. Students have to interact and cooperate during the semester in order to agree on the necessary specifications and on how to integrate all the elements of the solution from a technical, marketing and business point of view. The first face-to-face meeting runs for five working days during which students design a first draft of the solution for the challenge at hand organize themselves to work as a team during the semester and assign responsibilities to each team member according to the number of ECTS credits they get for their work. At the end of the week the envisaged solution by each team is discussed with the company, the teachers and the students so all agree on a definite proposal. After this first meeting, students work at their home institution working at a distance through online groupware platforms. At the end of the project all modules are integrated and the fully operational system, a unique product, is presented by the students as a team. The second and final meeting took place in Porto, Portugal 20-24 June 2002, students get together face-to-face again to finalize their solution, their final presentation and to discuss the delivered product with the client company and the teachers. The team as a whole must guarantee that all parts integrate well to produce a unique solution for the problem and present the full solution to the project jury. The project jury was composed by a teacher from each partner institution and a representative from the client company.
In total there were 7 projects implemented in the academic year 2021/22 and 3 of them will be presented where HMU students participated. The first project was suggested by Hylyght, a Belgian startup company. The challenge was the designing and development of a user friendly web-based application for physiotherapists, doctors, and coaches, which will help to quickly gather all the necessary information they need without losing time on testing or the analysis video. Company’s clients spend a lot of time on testing and gathering data. The analysis takes too much time and there are a lot of open-source options to assess these tests automatically. This holds them back, it’s always an effort to test and screen; even though objective data are more and more important. This application will help them by automating some of the tests and offer a user-friendly web-based app, which is linked to their cloud platform. The team was separate into the groups of marketing, design, and development under Scrum framework. For the organization and management of the groups tools like Trello, Microsoft Teams, Dropbox, and GIT were used. The IT group divided the requirements in smaller tasks in order to work on them separately. For the development of the website the JavaScript framework “Vue” and Vue's tools “Vuex”, Python, and HTML we used.
The second project was introduced by Epam Systems an American company that specializes in product development digital platform engineering, and digital product design and its branches are represented in more than 35 countries. The challenge was to create an interior design application, named “DecoratAR”, to allow people worldwide to visualize furniture in their living spaces more easily. This application is intended to be used both for professional and private use. The aim of the team was to combine all the features from similar applications on the market into one application for easier and more practical use. For the development of the application Unity3D was used for the code (with C#) and Blender for the models. The team stayed in touch through various platforms and programs like Microsoft Teams, Whatsapp and Zoom. The presentations were made with Canva and the mockups with Figma.
The third project was addressed by Expect Me is a Belgian hospitality tech startup that focuses on the international hotel industry. They provide hotels with a unique software that will allow their guests to select and guarantee a specific room based on a clear floor plan and room overview, as convenient as selecting your seat on a plane. The challenge was to develop an integrated plan for an automated onboarding process to activate those hotels on Expect Me, named “Onboard Me”. This project required building a dedicated onboarding platform, either custom-made or (partially) integrating open-source tools, considering a service approach, proper communication, marketing, and design to reflect Expect Me hospitality values. The team was divided into four departments: marketing, hospitality, design and development. The marketing department helped with the “Onboard Me” platform providing a mission, vision and values statements, a description of the platform and their benefits. The hospitality team was asked to create a data base with the over 600 hotels that the company provided and establish direct contact with some hotels located in Portugal that were on the data base. Moreover, the hospitality team helped with the making of the marketing action plan. The design team focused on corporate identity, flow diagrams, wireframes and website design. The development team implemented the “Onboard Me” application by developing and integrating three portals: Admin Portal, Company Portal and Customer Portal.
==> Abstract (PDF)Universities are encouraged to build partnerships and multidisciplinary projects based around real-life problems. Our project “Development of IoT-driven solutions for smart connected islands” is a multidisciplinary international project, executed by the students and lecturers of AP University of Applied Sciences and Arts and Karume Institute of Science and technology in Zanzibar.
Electrical energy supply and demand do not always match during the day as private households consume more electricity in the morning and evenings as during the day. Moving some of the electricity production to the renewable source such as wind or solar power generation does not alleviate this. A number of systems have been tried to use smart grids to better balance the load in the grid. A new system is proposed to use appliances in private households to improve load balancing in an automated fashion.
The proposed system controls standard household appliances, e.g. washing machines, to run the appliance at the most efficient time within a user set schedule. A simple networked plug together with an MQTT Broker is used to switch an appliance on or off. A smart phone app provides the user interface to set up schedules for the different appliances. The aim of the system is to improve the load balancing of the electricity grid, thus external data are fetched by the server to decide the best time for the appliance to run.
Human machine interaction in the digital era has become a mainstream form of providing and consuming services. We use it in self services of Medical treatment, Sopping platforms, Customer Service interaction, and recently for Education. I addition all Automated intelligence robots are using a model of conversation interaction as part of their operation such as autonomous Vehicles and Social Robots.
The dialog options vary from texting to chat bots, to speech agents and avatars all the way to robots and humanoids. Now that we talk about the dialog in the virtual world as well (metaverse) the importance of a relatively new filed called “Conversational Interaction” (CI) is crucial. It is a combination of several fields: Speech processing, NLP, UI and UX and using ML to enhance the dialog. The area of CI will involve the use of Multimodality approach which combines data and sensors to the interaction decision making module. The CL area is not only academic but deeply rooted in industry implementation.
In the digital, words like Innovation, Entrepreneurship and Digital Transformation are essential to every company’s echo system. New technologies in the area of Artificial Intelligence, conversational interaction, automated services must be integrated in organizational processes. Conversational Interaction if done correctly, to help a company be an effective in the interaction with customers building portals, tools, and platforms that allow rapid deployment of conversational systems.
==> Abstract (PDF)The norm of our societal life consists of various communication methods. However, senior citizens, young children, and people with age-related diseases often find it hard to express themselves. They are not fully aware of their need for help or how to ask for assistance. This lack of awareness decreases the quality of life and even endangers those individuals.
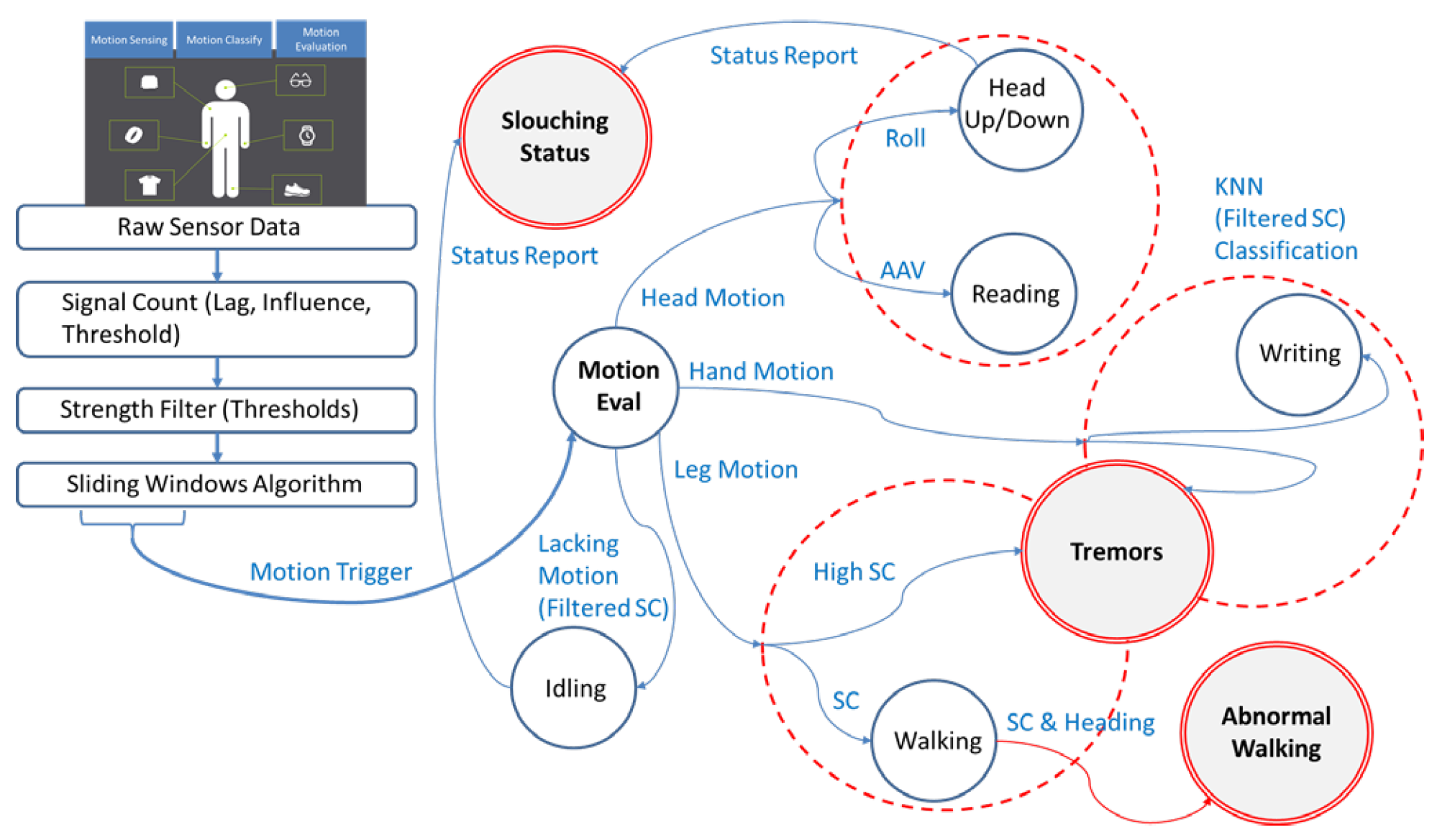
The primary objective of the IC-SAFE (Intelligent Connected Sensing Approaches for the Elderly) is to track the safety of the elderly by using various connected, intelligent wearable sensors. Dementia patients have been observed to perform specific actions, alluding to their need for assistance. In theory, an individual can recognize a lack of movement (a long idle status), the onset of aggression or tremors, and aggravated dementia due to depressive rumination as an issue. However, a patient with dementia will not be able to appropriately express their needs to a caretaker in a timely fashion. IC-SAFE consists of motion sensing, classification, and evaluation functions (Fig. 1). IC-SAFE provides an automated and minimally invasive solution for sensing initial symptoms of distress (both physical and emotional) by coordinating motion data, including walking gaits, arms and leg tremors, and long lounging positions to classify the safety status of dementia patients both physically and emotionally. Lastly, it alerts family members and caretakers about the situation before the symptoms foster a further diagnosis.
This project identifies several scenarios for dementia patients and proposes a few practical detection algorithms. It has been observed that patients with dementia perform certain repetitive motions, such as walking in a circle and sitting idle with their head bowed, in addition to the onset of other symptoms, such as aggravated tremors in the hands, knees, and ankles. We have obtained these motions to indicate emotional or physical status changes. We further characterized these actions as abnormal walking patterns and repetitive movements, specifically hand and leg tremors. To eliminate false positives triggered by reading books, regular walking, and handwriting, we have identified a threshold between similar actions, all of which have a high confidence rate.
Feasibility tests have been performed using IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) sensors in various positions, and data from these experiments have been gathered. We have proposed efficient real-time algorithms using analytical learning methods and identified several safety target scenarios by analyzing the corresponding gait data (Fig. 1). Although the current prototype is a basic experimentation prototype, it eventually targets to automate an Alive Inside [1] application as a future product. Alive Inside is a humanitarian project to revitalize the memory of senior citizens by playing cherished music of their youth (and memory). However, due to being a manual process, music cannot start playing when needed. IC-SAFE would be able to automatically sense emotions and play the right music for the patient (the music selection is another area of research - AI-driven precision music DJing) via bone-conducting headphones or intelligent speakers such as Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Award No # 2141131.
REFERENCES
COVID-19 has been causing several pandemic waves worldwide due to its long incubation period and hostile asymptomatic transmission. Society should continue to practice social distancing and masking in public despite aggressive vaccinations until achieving population immunity. However, the existing technology solutions, such as contact tracing apps and social-distancing devices, have been faced with suspicion due to privacy and accuracy concerns and have not been widely adopted.
This paper proposes a novel infection management system named Crowd-based Alert and Tracing Services (CATS) to build a safe community cluster. CATS applies social distancing and masking principles to small, focused communities to provide higher privacy protection, efficient penetration of technology, and greater accuracy. We have designed a smart tag for managing social distancing. We also implemented a Machine Learning (ML)-based face masking detection system for Modeling Safety Index in Crowd (Mosaic). Mosaic builds a new dense-mode crowd masking dataset to detect, count, and classify the crowd's masking condition and monitor social distancing.
In contemporary times, the concept of creativity needs no introduction, and the necessity to be creative in all areas of life is almost self-evident. In such a cultural environment, the ongoing immense popularity from which creativity benefits lends it considerable symbolic capital: Even after decades of academic research, creativity has withstood its de-mystification and still denotes secretive and mystically-inclined exclusivity and superiority. This subtextual semiotic relation often accompanies seemingly rational, democratized and well-elucidated references to creativity. In other words, this mental concept remains powerfully intimidating.
This talk draws on years of teaching creativity in academic settings, and contends that enlisting alternative and non-threatening terms in relation to creative exploits wield a reassuring and empowering effect on college students. Whenever possible, reformulating creative endeavors as serendipitous luck, methodical professionalism, psychological warfare, social privilege or technical achievement strip the concept of creativity from much of its angelic aura. In a pedagogical context, an increased awareness of the influence of speech on cognition and practice invoke an alternative rhetoric in order to refer to creativity differently. By virtue of being less daunting, a powerful critical stance of creativity’s lofty cultural status that tempers its admiration may be forged. This template can be used for designing emboldening cultural environments and modes of thought among students, and more generally among people who strive for an adequate mastery of the concept.
==> Abstract (PDF)Arthur C Clarke’s famous third law once argues that sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic. For consumers of innovative technologies, and sometime for its creators, this observation - even if obviously simplistic - may appear commonsensical.
This talk, eschewing a patronizing judgement over non-industrialized societies (also referred to as supposedly “primitive cultures”), discusses this argument from a professional anthropological perspective. It contends that, when comparing non-industrialized cultures to present-day industrialized cultures - especially regarding magic, religion, art and technology - similarities outweigh differences. Those include the human minds’ elective affinity for symmetry and binary structures; Human’s propensity for anthropomorphism (i.e the attribution of human-like features to non-human agents, notably in anthropomorphic technology); Human’s understanding of the manipulation of the natural world through magic; and most importantly, the concept of agency as related to objects of art. The latter draws on anthropologist Alfred Gell’s notion of “technology of enchantment” – the idea that the formation of an object of art’s fascinating qualities are related to the extent that the process through which they were created, is either absent or eminently visible. Eventually, such comparisons challenge both the conception that technology is deeply dissociated from supposedly non-rational modes of thought, as well as any reactionary longing for an imagined ideal “technology free” past – These insights hold meaningful practical implications for both creators and consumers in the realm of Ambient Intelligence, IOT and embedded systems.
==> Abstract (PDF)Traditional coronary angiography is an invasive method that can lead to safe results concerning the patency of the coronary arteries. Despite method’s high accuracy it has major drawbacks because it has risks for patient's safety. On the other hand, with the advancements of medical imaging, this invasiveness can be skipped, and the patient can be examined bloodlessly with CT coronary angiography. Although this method offers a major advantage, it lucks in accuracy. More specifically, some artifacts around the lumen of the artery lead to false evaluation of the patency of the coronary artery.
This research project aims to counterbalance this drawback and make CT coronary angiography safer for the evaluation of the coronary arteries patency. The task of the project will be addressed with Genetic Adversarial Networks (GANs). GANs -which is a Deep Learning model- are well-known for their ability to generate synthetic images. The project’s rationale is the development of an algorithm that can correspond a CT angiography to traditional angiography and thus all medical parameters that doctors need can be extracted with great accuracy.
==> Abstract (PDF)Medical suspect findings are spotted in medical images such as CTs and MRI scans. These findings may comprise of masses (malignant or benign), nodules or generally any space-occupying lesions. Subsequently, the patient follows a therapy and later is having new CTs or MRI scans to evaluate his response to the treatment in comparison to the previous state observed. However, this classic approach has a few drawbacks e.g., the doctor may not recognize suspect findings or evaluate them incorrectly. These drawbacks may be overcome with the utilization of a deep learning algorithm, which will be trained to identify suspect findings with high accuracy. Nowadays, the evolution of Deep Learning and its utilization in medicine is phenomenal and has been proved that can handle many medical tasks with great results. One of the main advantages of Deep Learning is that all necessary parameters are generated automatically in contrast to traditional Machine Leaning.
This research project aims to develop, deploy, and evaluate a deep learning algorithm which will take into account all patient’s parameters automatically, rather than manually. Thus, and without any human intervention and with the use of medical scans only, the developed algorithm will be able to track and evaluate patient’s current state of space-occupying lesions.
==> Abstract (PDF)The development of the modern computer age was strongly influenced by Mark Weiser (1952 to 1999) and his vision. The prediction that in the future invisible computers will be embedded in our everyday lives and the objects that surround us eventually led to his idea of ubiquitous computing (1988).
In his seminal publication, "The Computer for the 21st Century (1991, Scientific American)," he claims and hopes, "Specialized elements of hardware and software, connected by wires, radio waves, and infrared, will be so ubiquitous that no one will notice their presence."
Weiser's ubiquitous computing eventually led to the definition of the Internet of Things (IoT).
In parallel, the ideas of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Blockchain technology (BC) were amplified and finally found deeper meaning and wide application in their fusion with IoT.
In this talk, we will show how the symbiosis of AI, BC, and IoT is leading to new and powerful technological breakthroughs. Selected case studies will support this introduction. Selected case studies will support this introduction. However, a critical look at the so-called state of the art will also show that we are still far from Mark Weiser's visionary view of our future.