

Smartphones are emerging as useful health monitoring tools besides being important communication devices. Modern smartphones are equipped with several sensors, which are often exploited for fitness and wellness applications. Beside these internal sensors, there are certified medical devices and consumer products, which can measure and provide data to smartphones using new communication technologies.
This “Internet of Things” is a rapidly growing market that provides developers with novel opportunities in the health sector. While the prevalence of infectious diseases has declined in the last century (due to better hygiene, availability of antibiotics etc.), the prevalence of chronic inflammatory diseases, such as psoriasis, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel and rheumatoid diseases, has almost exponentially increased. Information like the clinical condition of patients, diet plans, physical activities, medication effects and reported quality of life are important measurements to study environmental factors that are important causes and modulators of disease but also to measure the outcome of and compliance to therapies. Moreover, the treating physician can monitor the patients’ health between the visits at his ambulance. However, the information between the visits is often inaccurate or missing. This communication gap between patients and physicians can be resolved by integrating smartphones and wearable sensors into a patient information system. As the age of onset for patients with chronic inflammatory diseases is generally low, our patient target group is ideally fit for an innovative smartphone App.
Our present work evaluates already existing mobile health concepts and we have developed a novel prototype application for data collection and self-management of chronic diseases. It collects information from the patients and autonomously from configured sensors for analyzing different lifestyle behaviors. As the wearable market is very large, we conducted a small benchmarking study of different suitable devices. The summary of this study will be presented. Important parameters related to health that can be measured with these sensors are also discussed. Once established, our system will aid in monitoring health and disease through providing a secure, scalable, modular and accurate toolbox.
TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X are radar Earth observation satellites, which are a joint venture between the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and Airbus Defence and Space. The satellites carry a high frequency X-band SAR sensor, which can be operated in flexible imaging modes in order to meet the requirements of versatile applications. A SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar Instrument) sensor scans the Earth’s surface from satellites with the help of microwave pulses. The satellites are controlled, operated, scientifically explored by DLR while the commercial exploration is undertaken by Airbus Defence and Space Germany.
Advantages of the TerraSAR-X services include flexible coverage and spatial resolution, excellent positional and radiometric accuracy, comprehensive network of ground stations, Direct Access Services ensure data delivery in near real time and WorldDEM (global Digital Elevation Model). TerraSAR-X images are widely used for Science & Industrial prospects including Defence & Intelligence, Oil/Gas Site Monitoring, Asset Mapping for Insurance Agencies, Maritime Monitoring, Forestry & Agriculture, Public Safety and Land Administration. Direct Receiving stations (DRS) located throughout the world help in receiving TerraSAR-X images in Near Real Time. Direct Receiving stations are equipped with Multi-Mission terminals which can also be used to receive optical imagery of SPOT and PLEIADES satellites.
TerraSAR-X image products can be acquired in five main image modes with flexible spatial resolutions (0.25m / 1m / 3m / 18.5m / 40m) and scene sizes (5km to 400 km swath width). Two satellites, TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X orbit the Earth in a unique formation with distances down to only a few hundred meters. They acquire the data basis for the WorldDEM - a unique global Digital Elevation Model of unprecedented height quality, positional accuracy, and spatial coverage. WorldDEM is the new standard of global elevation models and will be available for the Earth’s entire land surface - pole to pole.
Industrial pollution in urban areas, fossil fuels from vehicles and buildings can result in rainwater pollution. Additionally, dust, solids, and fecal deposits from birds and rodents, which accumulate on rooftops during dry periods, may also affect the quality of harvested rainwater. Therefore, the first-flush of the roof runoff water; i.e. the first water volume of the rainfall event, may contain pollutants at increased concentrations.
This paper presents a roof rainwater harvesting system, which uses fuzzy logic control to convert the direction of the runoff water, between two tanks, which collect, filter and then forward the water for reuse. The purpose is to separate the first flush rainwater from the remainder, i.e. the black from the grey water respectively. The presented system is a part from a larger open source autonomous water-waste management system which was installed on a building located at an urban area of Crete in southern Greece.
The purpose of this paper is the development of a system, consisting of hardware as well as software, which provide the ability of communication, interaction, and data exchanging between a user and remote devices and modules. Many times, has been noted the necessity of accessing digital devices that are located remotely and either hold information that we need to know or waiting for data from the user for executing specific commands. Examples are sensors, microcontrollers and switches which find numerous applications from automated houses to robotic systems and weather stations. The system that was developed in this paper is a mediator between such user requirements and digital means such as those mentioned previously.
Part of this paper was carried out by using the development board, Virtex-6 CXT FPGAs, which hosts a FPGA for the implementation of the necessary hardware. The design of the hardware as well as the development of the code executed by the embedded system of this paper was accomplished by using the Xilinx Platform Studio suite. More code was developed with Netbeans platform for the creation, in Java language, of the necessary applications which give the remote user the opportunity to interact with the embedded system. There were also used sensors, microcontrollers and other electronic means to document the efficiency of the systems. The result was the successful development of a system that overcomes the plan originally envisaged. This work, composed of the embedded system and applications to the user and server terminal, delivers web services to communicate with remote devices and components in the context of reliability and flexibility.
TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X are radar Earth observation satellites, which are a joint venture between the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and Airbus Defence and Space. The satellites carry a high frequency X-band SAR sensor, which can be operated in flexible imaging modes in order to meet the requirements of versatile applications. A SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar Instrument) sensor scans the Earth’s surface from satellites with the help of microwave pulses. The satellites are controlled, operated, scientifically explored by DLR while the commercial exploration is undertaken by Airbus Defence and Space Germany.
Advantages of the TerraSAR-X services include flexible coverage and spatial resolution, excellent positional and radiometric accuracy, comprehensive network of ground stations, Direct Access Services ensure data delivery in near real time and WorldDEM (global Digital Elevation Model). TerraSAR-X images are widely used for Science & Industrial prospects including Defence & Intelligence, Oil/Gas Site Monitoring, Asset Mapping for Insurance Agencies, Maritime Monitoring, Forestry & Agriculture, Public Safety and Land Administration. Direct Receiving stations (DRS) located throughout the world help in receiving TerraSAR-X images in Near Real Time. Direct Receiving stations are equipped with Multi-Mission terminals which can also be used to receive optical imagery of SPOT and PLEIADES satellites.
TerraSAR-X image products can be acquired in five main image modes with flexible spatial resolutions (0.25m / 1m / 3m / 18.5m / 40m) and scene sizes (5km to 400 km swath width). Two satellites, TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X orbit the Earth in a unique formation with distances down to only a few hundred meters. They acquire the data basis for the WorldDEM - a unique global Digital Elevation Model of unprecedented height quality, positional accuracy, and spatial coverage. WorldDEM is the new standard of global elevation models and will be available for the Earth’s entire land surface - pole to pole.
One of the main agricultural products of the Mediterranean countries is Olive Oil and it major enemy is the olive-fruit fly. To face the aforementioned threat, current practice in Greece is to apply a protein based solution from the ground using a small scale tractor. The efficiency of this method is based on the proper identification of the insect’s population. Currently the information available is based on McPhail traps deployed in the field. The number of insects inside the traps is the key factor for deciding whether the farmers will spray or not.
In previous work we have introduced an electronic McPhail trap, which had the ability using a custom embedded system to transmit the information from its interior to a remote web server and then based on the observation of a human expert take proper actions. In this work we present the development of a software module running on a remote web server, which allows to automatically count the insect inside the traps and give an exact estimate about the number of insects. This module renders the need for human intervention and assist the farmers to decide whether they will spray or not. The efficiency of the proposed methodology was tested using a large sample of real field data.
Child protection is one of the most critical issues of public safety. However, keeping track of one’s young children is often a difficult and daunting task for parents. The need is especially intense for parents with special-needs children or when they are away at work. It takes a village to protect a child, and a crowd can be powerful. As a social effort to track missing children, the AMBER Alert Program is intended to galvanize an entire community to assist in the search for and safe recovery the missing children. While the Program’s coverage of social monitoring has significantly broadened in recent years including phone messaging and online social media, due to the nature of multiple steps of human involvement, successful recoveries are often far too slow, the success rate is very low, and the process is costly.
We automate the process of both the search and report, and radically improve the effectiveness of child monitoring and searching through innovative wireless and cloud technologies, especially for the smart and connected communities. The project is to effectively and efficiently utilize crowds to protect children using technology that provides a faster, better and less expensive solution. The project involves developments of WiFi tags for young children, smartphone apps for parents, caregivers and volunteers, and a cloud server. The project addresses several social and technical issues including effective and wide sensing coverage, privacy of identification and location for children, volunteers, and parents, small and affordable tags for underage children, low energy consumption of tags, data security in a cloud server. The core set of methods and processes of the project can be replicated, adapted and used in other crowd sensing applications in smart and connected communities.
Developing an all-terrain legged robotic platform capable of maneuvering and navigating in a non-structured environment has been an area of research in recent years. This paper presents the analysis, design, and implementation of an indoor/outdoor robotic motion platform which is intended for use in intelligent autonomous robots. The platform will provide a stable motion system for robots equipped with various sensory systems, to perform tasks autonomously to reach a goal.
For the development of this all-terrain robotic platform, we use two ARM Cortex M4 microcontrollers using a Real-time Operating System (RTOS) as well as a simple sensory system. The communication between the microcontrollers was established using the Controller Area Network (CAN) protocol as well as a novel encryption/validation messaging protocol above it. Moreover, a novel memory allocation scheme was analyzed and used, providing efficient dynamic memory allocation and defragmentation for embedded systems lacking a Memory Management Unit (MMU). Using as main criteria the efficiency in handling both external and internal memory fragmentation, as well as the requirements of soft real-time applications in constraint-embedded systems, the proposed solution of memory management delivers a more precise memory allocation process. This scheme is evaluated providing encouraging results regarding performance and reliability compared to the default memory allocator. Finally, using Inverse Kinematics algorithm we are able to translate any change of the body’s position into changes of each leg position, thus we are able to work out the angles of each servo-motor.
The outcomes of these endeavors would apply to problems in harsh environments, for example, in space research, investigating the surface of a planet without endangering human lives, or in disaster areas to locate injured persons and to give rescue personnel a more detailed picture of the area. The work done includes the initial development of a five-legged robotic platform containing a discrete-event based motion controller as well as a communication system providing an interface for easy handling the motion system whereby providing a more realistic experience of teleoperation, remote sensing, and semi-autonomous robot behavior than what currently exists. – While it is too early to incorporate the current research results into a final product, this development is specially designed on a smaller scale which can be used in mock system trials instead of toy-based robots, thereby providing more accurate representations of the challenges encountered by full-sized robotic automation systems.
The work completed to date acts as a starting point from which improvements and extensions could be made and incorporated. In this regard, suggestions for future work are also presented.
Professional life is nowadays heavily depending on mobility and demands professionals to excel in communication skills at an international, cross-cultural environment. However, soft skills, as well as international exposure, are rarely addressed by undergraduate courses.
Within the framework of Erasmus +, Strategic Partnerships, the project “Blended Academic International Mobility (Blended AIM)” started in October 2015 addresses such issues. In particular, each year a project course will be implemented where students from distinct but complementary areas of study will develop a complete solution for a problem proposed by a company. Students will be working as a multinational, multidisciplinary team with the common goal of delivering by the end of the course a product following the company requirements. Students will meet face to face at the beginning of the semester to get to know each other, to get acquainted with the problem to solve and to agree on the best way to work during the semester. Then they will work at their home institution, cooperating through online tools. At the end of the semester, students meet face to face again to present the product developed by the team and to be evaluated. The aim of the project is to remodel international mobility and empower students’ employability by means of blended mobility. The goal of Blended Aim 2016 was to develop a web application based on the principles of the PRINCE2 method.
PRINCE2 is the method that provides businesses a clear view of a new project, as it examines the possibility of its success or its failure before it begins. Main components of this project is a printed canvas divided into several different sections, like benefits, risks, product owner, suppliers, etc. Every team member of the project can participate by writing his idea on a note and stick it on the canvas in each section. The only problem with this process was that all team members should have their physical presence in the same room with the others at the same time. Thus, the students of Blended Aim 2016 were asked to implement and improve the printed version of the canvas to a web-based canvas. On this web-based canvas all team members can add a note to a section, have simultaneous collaboration and use other features, like planning poker from different places in the world at the same time, or not.
The students were divided into three scrum teams and the application was divided into three main sections, the landing page, the dashboard and the canvas. In each of this sections a team was assigned. The students of TEI of Crete worked on the frontend of the application. Their main tasks were the implementation of the design for the landing page, including all the functionalities such as animations, effects, responsiveness, register and login-logout, and the dashboard, including responsiveness and user profile. In the canvas section their tasks were to add member management such as adding a member to a canvas, view canvas current members and delete members. Along with those tasks they were also assigned to add the ability to send default emails after specific actions were made such as registering. To implement the tasks, technologies like AngularJS, jQuery and Bootstrap were used.
Research on power management in Servers can ease the installation of the Data Center, cost reduction, and environmental protection. In order to evaluate the thermal performance and energy efficiency of buildings and building sub-sectors, several simulation tools have been proposed. In this work, the researcher exploits the potential of EnergyPlus software. EnergyPlus is a software platform that is used in relation to other tools in order to create a simulation environment. In order to develop a modeling procedure, the researcher studied the simulation tools and used them in order to create and simulate a data center space in an Educational building in Heraklion, Crete.
The Control Systems & Robotics Lab at the Technological Educational Institute of Crete has developed an anthropomorphic robotic hand intended to function as a general-purpose research tool for the study of machine dexterity and the grasping of objects. TALOS is the name of the robot hand, which has a thumb and four fingers with total 16 degrees of freedom (d.o.f). The joints are driven by RC-servo motors that are hosted in the phalanges and the palm of the hand. The later simplifies the mechanical configuration of the joints while the great advantage is that a common RC-servo controller can independently control the servo actuators of the joints. The manufacturing proses, the mechanical configuration of the joints and the assembly of the robot hand are also explained in detail along with the control architecture which is divided into two levels and is based on the kinematic model of the robot hand. Finally experimental results are given to evaluate the practicability and effectiveness of the robot hand in grasping objects and mimicking human gestures.
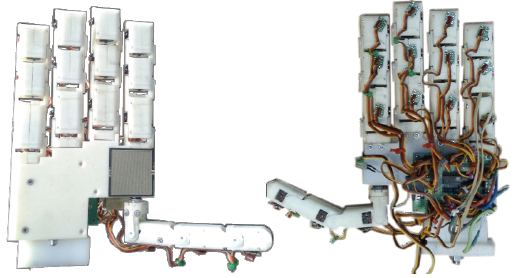 The Robotic Hand TALOS
The Robotic Hand TALOS
With the rapid population ageing in Europe and in Denmark, there is an increasing interest in technologies and designs that can support the elderly citizens in sustaining well-being and health along with preventing functional decline [1]. To date, the designs of lighting systems in elderly housing are simple and primarily made to support only visual acuity without taking into account other parameters [2]. But elderly people have higher demands on quality of light as their body has to cope with immobility, pathologies and age-related functional decline [3].
In this context, this paper investigates the development of a personalised and adaptive intelligent system [4] to adjust the lighting design in order to improve well-being and comfort levels, as well as to meet the needs of elderly people at home. To this goal, circadian adjusted LED-based (CaLED) lighting is used, which can reflect the rhythm of out-door daylight. CaLED lighting seems that may positively influence age-related needs, mood, cognition, alertness, sleep and improve well-being in general [5][6].
To build this intelligent system 3 different types of data are considered and cross-checked: a) medical (biofactors), b) sensor-based (activity detection, actigraphy, etc.) and c) anthropological (mood and behaviour). This way, the effect of circadian lighting on well-being, can be also documented, before this new technology can be recommended for implementation in elderly housing. A test installation is planned at “Sundhedshuset” in Albertslund, Denmark: 15 flats with frail elderly and 9 flats with people with dementia are used.
| [1] | Lynch, J., & Draper, H. (2014). Ageing well with technology. University of Birmingham |
| [2] | Schlangen L, Lang D, Novotny P, Plischke H, Smolders K, Beersma D, et al. (2014). Lightning for well-being in education, work places, nursing homes, domestic applications, and smart cities. Accelerate SSL - Innovation for Europe. SSL-Erate. Available from: http://lightingforpeople.eu/2016/wp-content/uploads/2016/03/SSLerate-3.2-3.4-v4.pdf. |
| [3] | Mobily PR, Skemp Kelley LS. (1991). Iatrogenesis in the elderly. Factors of immobility. J Gerontol Nurs. Sep;17(9):5–11. |
| [4] | Gate 21, Abertslund Kommune, Amager-Hvidovre Hospital, Zumtobel, AAU Copenhagen. (2015) LighTel project. Available from http://www.gate21.dk/project/lightel/ |
| [5] | Turner PL, Van Someren EJW, Mainster MA. (2010). The role of environmental light in sleep and health: effects of ocular aging and cataract surgery. Sleep Med Rev. Aug;14(4):269–80. |
| [6] | Kuijsters, A., Redi, J., de Ruyter, B., & Heynderickx, I. (2015). Lighting to make you feel better: Improving the mood of elderly people with affective ambiences. PloS one, 10(7), e0132732. |
In this paper, we present the development of a novel deep learning implementation framework for image classification applications. This work focusses on the transition between pure experimental deep learning methods, towards deep learning based applications that can be used from any user. Our proposed framework consists of two parts, the CNNs-Tester a deep network training desktop application and a web-application called PaternF. The desktop application is able to use sets of images depicting individual categories in order to train a convolutional neural network (CNN) model. Our desktop application can provide statistics about the quality of the given training image set, as well as, the training procedure of the user-defined model. Furthermore, CNNs-Tester provides an offline CNN model testing operation where users are able to perform probability tests using unknown images, relative to the categories used in the training process. The resulting CNN models can then be used by our proposed web-application termed PaternF. When using our user-friendly web environment, the user can perform online image categorization by uploading any query image. Our web-application will output a class identity for the query image calculated from the CNN model. Finally, we will also present some use-cases that support our claims for the user-friendly capabilities of our novel deep learning implementation framework.
Remote control of mechatronic systems is widely used not only in research, but also in the industry. Tele-operating a machine can enhance the safety of the operator and even the dexterity of the system, as well. However, using wireless control can sometimes be complex and harsh. In addition, remote control of robot manipulators and anthropomorphic robotic hands, in an intuitive way, is not an easy task. In this proposal, we introduce the teleoperation of a 16 degrees of freedom (d.o.f.) robotic hand. The system is based on a custom-made data glove that is equipped with 11 flex sensors in order to capture the motion of the thumb and the rest of the fingers of the operator’s hand. Moreover, by using a wireless end-point communication the robotic hand can be operated wirelessly. Furthermore, experiments were conducted to test the capability and applicability of the system. Ultimately, the data glove can track the movement of the operator and subsequently move the robotic hand. The system can execute subtle gestures; also grab objects with different geometry.
Automatic localization of target objects in digital images is an important task in Computer Vision. The Generalized Hough Transform (GHT) and its variant, the Discriminative Generalized Hough Transform (DGHT), are model-based object localization algorithms which determine the most likely object position based on accumulated votes in the so-called Hough space. Both algorithms have shown state-of-the-art performance in tasks of limited object variability, e.g. iris or epiphysis localization. However, many real-life object localization tasks - e.g. pedestrian localization - involve various kinds of object variability hampering the localization task. Here, we address two sources of variability: Background variability, i.e. image edges not belonging to the object of interest (e.g. from other objects, background clutter, noise etc.) and object size variability (i.e. the object of interest appears with strongly different sizes in the images). Both sources of variability can cause misleading votes which increase the probability of localization errors.
We investigate strategies to handle these sources of variability within the DGHT framework. Specifically,
we evaluate structured edge detection proposed by Dollar et al. as input to the DGHT and propose a model scaling
approach to handle different object sizes. In preliminary experiments we show that these two techniques have
the potential to significantly improve the DGHT localization performance in a pedestrian localization task.
The device records like any other device video, audio and other real world events to be sold by the creator. Inside the device a number of the main recording event monitoring devices and sensors it is installed like: microphone, GPS receiver, weather station, sensors, back camera, device serial number, fingerprint capturing, heart rate monitor and thousands more. All these data are embedded into a media-file. From this file we distribute the useful video, audio, image part to the internet and we keep the auxiliary file containing the forensic data. When falsification occurs the Court reverse the procedure and reveals the truth. There are two device benefits: First the recording occurred in the past (offline files) only falsification reveal is possible but with during online streaming transmission (online mode) we can instantly verify a genuine recorded event. Second most of the original auxiliary event data do not longer exist after the recording moment and cannot be falsified either alone or in correlation with other original data. Indicative applications are Forensics Auditing, Copyright Clearance, Personal secure recorder, Military SIGINT and Defense systems.
The importance of life-long learning is rising with the rapid development of technology and the changing competence requirements for engineers. Degree programme in Information Technology has offered a part-time program for several years to support life-long learning to students already employed and seeking for opportunities to study a Bachelor of Engineering degree in Information Technology. The existing curriculum and current pedagogical methods have some impediments resulting in poor success rate of studies. As a result a new multiform curriculum was developed which is based both on online education and new pedagogical methods.
This paper describes development and implementation of the new curriculum for multiform studies in degree program of Information Technology in Helsinki Metropolia University of Applied Sciences. The degree program is a four year bachelor's level program. As free university level online education is gaining popularity it is also facing severe problems with the success rate of completed studies. Despite the challenges online education provides unique opportunities for multiform education. The key elements are coordinated online education and project based learning. Additional motivation and dedication to the studies is provided by study groups to which each student belongs. This enables online peer-to-peer review and support combined with regular onsite meetings within the group. The new curriculum will be implemented in academic year 2016-2017.
One of the fundamental elements in the multiform education is high quality free online education provided by universities. As an example a free massive open online course in software engineering provided by University of Helsinki is introduced as well as the implementation of the course as part of multiform studies.
To prevent massive piracy in the Android app markets, Google provides developers the License Verification Library (LVL) to implement a network-based license checking service. The application queries the Google Play app, which builds a license checking request to a trusted Google licensing server, to obtain the license status for the current user. Since this library is written in Java, it cannot protect the app from reverse engineering. In this paper, a native LVL implementation in C is proposed. This native LVL is much harder to be disassembled into comprehensible code than Java. We introduce so-called fusing options to fuse the Android app and native code together while allowing different program parts to communicate by indirect method triggering. The result is that the app cannot be executed without it anymore.
Android is a target of software piracy. Application stores are trying to counteract piracy attempts by providing license verification libraries but even those do not stop theft of intellectual property. The scope of this paper is to present different attack methods. Insights to the attacks can be used to create countermeasures that are addressed shortly, while presenting their details in another paper (of this conference) instead.
Linear wire dipoles are some of the oldest antennas and for several applications the most versatile ones. Some of their advantages are: omni directionality, simplicity, easy fabrication, and low cost. Dipoles may be used as standalone antennas, but they are also employed as feed elements in several types of more complex antennas.
In the literature, an increasing number of artificial neural networks (ANNs) are built for the analysis and synthesis of various electromagnetic wave propagation, radiation and scattering problems. So, in this work we propose an alternate approach to the dipole antenna radiation problem using ANNs, avoiding the associated lengthy and time-demanding mathematical analysis as well as the use of 3D full wave software.
The results obtained from the neural network array models were compared to those from the analytical method and found in close agreement. The proposed method can predict with high accuracy, in less time and with minimum computational resources, the performance characteristics of the dipole antenna.
An increasing number of artificial techniques have been built for the analysis and synthesis of various electromagnetic wave propagation, radiation and scattering problems. In the present work a neuro-fuzzy system (ANFIS) is developed to estimate the radiation characteristics of a travelling wave
dipole antenna.
ANFIS has emerged as the combination of two powerful intelligent techniques: the artificial neural networks and the fuzzy logic approach, which have been adopted and tested to solve many real-world problems in recent years. This combination of fuzzy logic and neural networks into adaptive network architecture is the main fact making ANFIS so attractive in our investigation. Specifically, ANFIS integrates the greater learning capability of neural networks with a fuzzy logic approach to construct a
fuzzy inference system, with membership function parameters, which are tuned using a back-propagation algorithm either alone or in combination with a least squares method.
The proposed method is an alternate approach in order to avoid the associated lengthy and time-demanding mathematical analysis needed for the evaluation of the travelling wave antenna radiation characteristics. The presented model gives accurate results, having the distinct advantage that, after proper training, it completely bypasses the repeated use of complex iterative processes for new data presented to it.
This paper explores the differences in the state of the human brain when immersed in Virtual Reality (VR). VR has received a lot of academic, corporate and public attention in the past two years with the release of the first wave of mainstream, publicly available and affordable devices. Very little research has been done, however, in the effects of the use of such devices on the human brain. This paper proves there are differences in the brain activity when using VR as opposed to more traditional media and provides an estimate on their extent. Towards that end the brain activity of a group of 18 volunteers, 18-25 years old, male and female, was measured using a highly accurate, 14-channel, research-grade Electroencephalographer (EEG).
The measurements were first performed while the subjects were idle, then as they were using a classical, first person game via a monitor and finally when they wore a VR headset (Razer OSVR Hacker Dev kit) while experiencing a custom, realistic 3D environment. These measurements were then translated into six mental states, Engagement, Excitement, Interest, Relaxation, Stress and Focus while taking into account the individuality of the human brain. The differences in these mental states between the three activities (idle, monitor, VR) were calculated and presented using summary statistics. Outliers were taken into account and other methods were implemented to ensure data quality. From the six mental states, the one most affected by the use of VR was Excitement with a mean difference of 26.4% between the VR and the traditionally experienced environment, followed by Focus with an increase of 14.5% and Interest increasing by 12.1%. Stress levels were also elevated by 13.3% while using VR. All in all, experiencing a digital environment in VR is more interesting, much more exciting and increases focus, at the cost of a more stressful overall experience.
In this paper the capacity of the Air-to-Ground and Ground to Air system is studied. The Outside Cell Interference Factor is estimated through simulations for uplink and downlink. The calculation algorithm is explained as well as the scanning mode of interfering cells around the desired cell. Results for the number of active users for various values of the maximum height of the cell and its radius are presented. A Case Study for the Athens, Thessaloniki and Iraklio airports has been made in which the number of the users per cell is being calculated for voice service of 12.2 kbps and video calls of 64 and 128 kbps.
This paper presents the development of a low-cost embedded controller for the pendubot system. The pendubot is a two-link underactuated mechatronic device, frequently used for research and education in nonlinear control and robotics. The embedded controller employs the 8-bit Arduino Mega 2560 development platform, along with a custom-designed i/o board for interfacing with the pendubot plant. The developed firmware of the unit allows for balancing the pendubot in three different positions, by implementation of a gain-scheduled linear state feedback control law, designed via the linearized dynamic model of the system. The control loop runs at a 1.25 kHz rate, attained by low-level programming of the microcontroller. A serial interface enables capturing and displaying in real-time on an external PC, data regarding the system response, for assessing and tuning the control performance. Overall, the developed embedded system represents a compact-sized and cost-effective platform for digital control implementation
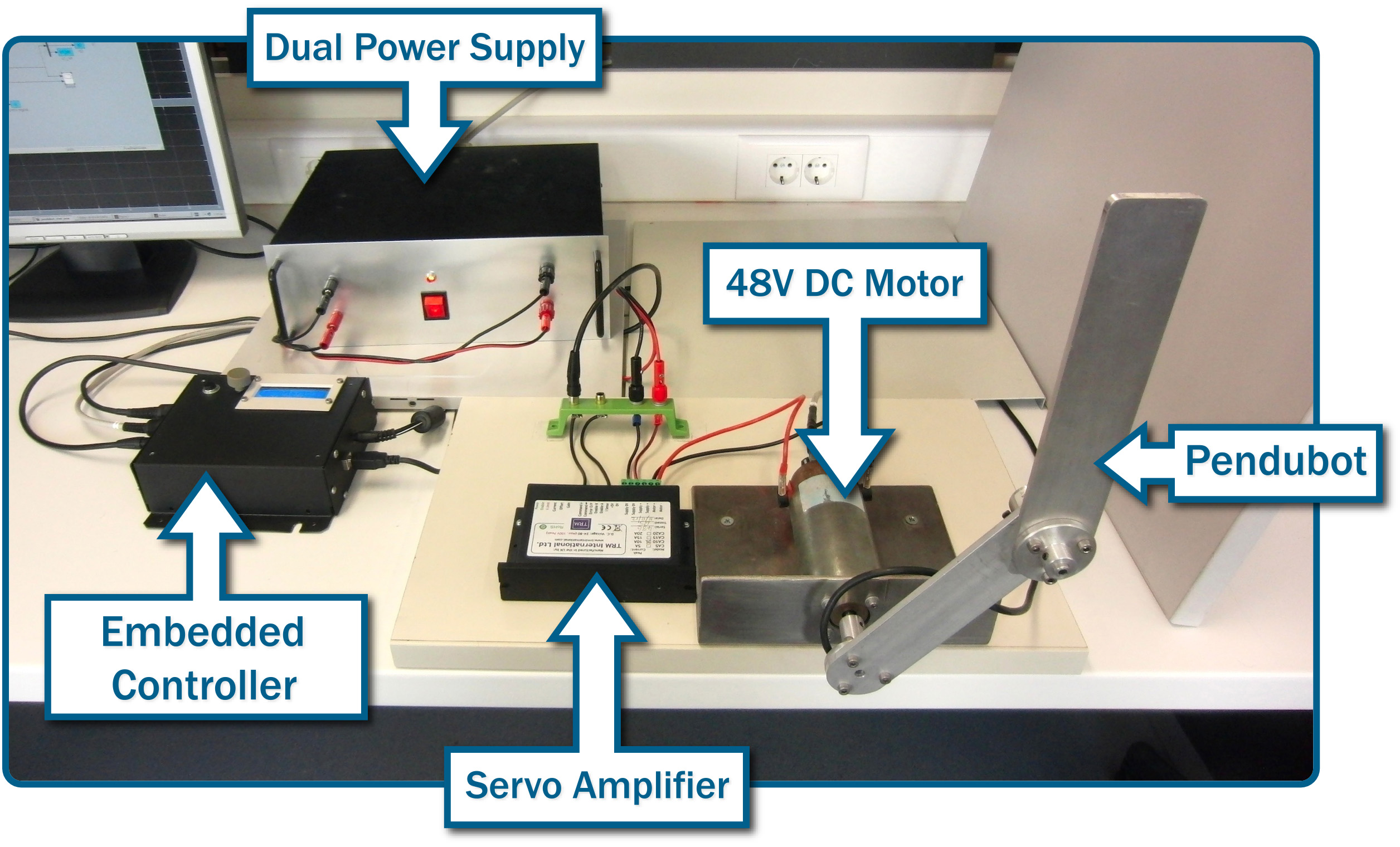 Figure 1. Overview of the pendubot control system.
Figure 1. Overview of the pendubot control system.
The CTAG face2|4 Audio Card is an I 2 S multichannel soundcard based on the AD1938 audio codec which supports two 24 bit stereo inputs and four 24 bit stereo outputs and was designed by Creative Technologies AG (CTAG) Fachhochschule Kiel (Kiel University of Applied Sciences). To use the soundcard, we have decided to use a BeagleBone Green (BBG) due to its Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP) which supports the timedivision multiplex protocol to transfer audio data with more than two channels over one single data line. A Linux driver model was developed, supporting the face2|4 on the BBG. Driver sources were committed in the upstream BeagleBoard kernel after a successful pullrequest on Github. Both, the new hardware and the software drivers for the BBG bring together a new kind of audio system that can be used for mobile or embedded applications (e.g. Eurorack modules).
One of the goals was to provide an open audio platform for musicians and other artists which requires a minimal latency. To address this goal, we have evaluated the ideal buffer sizes to achieve small latencies and avoid buffer underruns or overruns (XRUN). The minimum buffer size is 68 frames which causes a roundtriptime of ≈ 3.2 ms (measured with an oscilloscope). Moreover we have used a crystal oscillator with a frequency of 24.576 kHz. With this configuration we have achieved a maximum sample rate of 96 kHz with 8 audio channels. To get even higher sample rates (192 kHz) the soundcard can be configured via software to only use four output channels. Furthermore the audio system uses asynchronous sample rates for capture and playback (for example you can record with 192 kHz sample rate and playback with 48 kHz). The software drivers are compatible with Advanced Linux Sound Architecture (ALSA).
Feature overview:
Building ventilation are designed to provide air at comfortable temperature and humidity levels and to keep the concentration of air pollutants low. The ventilation process includes bringing in outdoor air which is often filtered and/or conditioned and distributing the air throughout the building. In the process roughly equal amount of indoor air must be exhausted from the building. Unbalanced air flow will lead increase in air flowing in/out of the building through other channels than ventilation ducts. This uncontrolled air flow may bring pollutants in to the indoor air or increase humidity in the structure of the building which may lead to structural damage and/or increase in pollutants in the indoor air. This paper proposes a sensor network that measures pressure conditions in a building which can be used to adjust and optimize the airflow in a building.
Important design issues for a wireless Internet of Things (IoT) implementation include the size and cost of IoT devices, the cost and communication performance for the connectivity of IoT nodes, as well as the energy management framework for the IoT applications (including the case of power provision through energy harvesting). However, more or less, most of the aforementioned design issues lead to deployment challenges from a wireless communications point of view.
Thus, this paper tries to address two major deployment challenges as they relate to the spatial distribution of both IoT nodes and energy harvesters by stochastic geometry modeling. In particular, various spatial point process models are presented and their suitability for the IoT ecosystem is examined. In other words, our aim is to propose the appropriate spatial point process model for specific IoT scenarios. In such a way, the performance analysis carried out with the aid of the stochastic geometry mathematical paradigm facilitates useful insights for IoT network deployments.
Since its inception in 2008, Arduino has conquered the embedded systems market due to its ease of use, low-cost point and extension possibilities. Arduino is used in many contexts ranging from education and hobby use to professional embedded applications. One specific application of Arduino has been in the audio and music domain. There exist several open source projects, where digital signal processing (DSP)-based audio synthesis code has been implemented using Arduino. One of which is the Arduino library Mozzi (http://sensorium.github.io/Mozzi/), which implements classes for various Arduino derivatives to synthesize and modify sound.
We have built a generic hardware user interface including a full octave + 3 notes fingerboard using capacitive sensing, 8 digital push buttons, 8 potentiometers and various LEDs which can be used in conjunction with Arduino as a music synthesizer platform or midi controller. For capacitive sensing the Microchip CAP1188 IC is used, GPIO extension ICs from Microchip (MCP23S18) are partially used for LED driving and push button read out. The analog to digital converter (ADC) MCP3008, also by Microchip, is used for read out of the potentiometers. A 2-layer printed circuit board (PCB) has been designed using the open source electronic design software KiCad. Its dimensions are 10cm squared.
Arduino classes to access all above mentioned periphery have been created and, in combination with Mozzi, several demo applications have been implemented. Amongst those are a midi controller, a sample-player, a drum machine, a micro synthesizer and a step sequencer. All those mentioned examples are able to run on low-cost Arduino Nanos. In addition, a library to use external SRAM and FLASH memory has been created which allows in conjunction with more powerful Arduino derivatives such as the Teensy 3.1 the implementation of delays, reverbs and samplers with reasonably long sample times. An initial demo video can be found in the projects section of the Creative Technologies working group home page http://www.creative-technologies.de .
Ria de Aveiro is a shallow lagoon, located in the Northwestern Portuguese coast, where traditionally salt was produced by evaporation in saltpans areas. Recently, Salicornia ramosissima, a high value plant able to grow in salted environments, started to be cultivated in saltpans replacing the salt production. Currently, the cultivation of this salty plant requires laboratory analysis to evaluate the fundamental conditions of the soil for a healthy growth of Salicornia ramosissima, in particular the salinity. In order to improve the process, avoiding this workload and getting more data to improve the studies, monitoring is required in the saltpans: salinity of the water, salinity of the soil, water level and other variables. As the saltpans in Ria de Aveiro are not easy to power, a decision was made to use a low-power IoT communication technology to develop sensors for this purpose.
It was decided to use Sigfox, a recent LTN (Low Throughput Network) operating in the ISM band. In this paper an overview of the requirements to automate the growing process of Salicornia ramosissima is presented. A summary of Sigfox technology is also included. The core of the paper consists of two parts, first a work in progress reporting the current architecture of the saltpans technology and the challenges found to develop the adequate sensors. Second, an evaluation of the coverage of Sigfox in the Ria de Aveiro area.
In the paper it is also reported the device already developed which includes a GPS and an accelerometer thus enabling a plug&play architecture for the sensors and alarm against unauthorized removal.
Engineering related fields are less attractive for the youth. There is, or they will be a shortage of qualified engineers. Engineering education is quiet demanding and drop out is quiet high. In Vaasa University of Applied Sciences (VUAS) many attempts are made to attract more students (VAMK yourself program) to increase the quantity and to keep them motivated all long the 4 year engineering programs through the 55 ECTS model to achieve the quality. In order to balance between quality and quantity it was necessary to create an educational scheme that is flexible and gives all types of students to develop their learning in an effective way.
In 2014 VAMK launched the Industrial Innovation Academy (I2A). Industrial Innovation Academy (I2A) is a structure that acts as a bridge between education and industry, to challenge students with real problems. The goal of I2A is to create an environment where students could develop better professional skills and work on real projects provided by the industry as well as develop own innovative ideas for the industry. The I2A with the feedback from the industry evaluate the students work and can provide the student with equivalent ECTS. A personnel study plan (PSP) is usually made as a contract for students who choose to take part of their studies at the I2A. In this presentation the speaker will tell about the methods used in the academy to help students achieve their learning goals, he also will discuss the difficulties in adopting such methods and finally demonstrate some project that has been developed under the guidance of the academy
This article highlights a new and low-entry system to use Bluetooth Low Energy beacons to share information about anything, to anyone, by anyone. The authors want to express the features and advantages of this new system, share the outcomes of preliminary experiments with different user groups and some new fields of application. Finally the article considers the educational and commercial value of the system which is used as a practice enterprise for public – private collaboration.
In the home automation the KNX system has, on the one hand, a large market share concerning industry, but it is on the other hand very expensive for private use. As electronic sensors are very cheap we have built an embedded application which creates a smart home based on embedded platforms (Rasp. PI, Arm MBED, Arduino). Then we couple this application to a basic KNX installation, which has its own protocol. The smart home can be operated through an app or website.
In collaboration with the agriculture department we have created an embedded measurement system that monitors the growth conditions of an algae breeder reactor, which is located in a greenhouse. We measure the temperature (infrared) of the water and determine the colour of the algae. On the basis of the collected data the food for the algae can be regulated. We also measure – in a matrix structure – the temperature and humidity on three different levels in that greenhouse. With a web interface you can input the desired settings and call up the data. In a second phase the data is shown in a three-dimensional image.
The Phaistos Disk, c.1700 B.C., is the Enigma of Minoan Crete (c.3200-1200 B.C.). It was found in 1908 by Italian Archaeologists in South Crete and dates to c.1700 B.C., i.e., half a millennium before the Trojan War. Minoan Crete is where mythology meets history. The Phaistos Disk has 242 signs, 61 words, on sides A and B, and probably consists of 18 rhyming verses. It has now been possible to literally ‘Read’ more than 90% of the Disk, by using Mycenaean Linear B and epigraphic continuity. While it is also certain that the text is religious due to parallel texts, i.e., other Minoan Linear A syllabic inscriptions of a religious nature.
This talk will present the ongoing results of 8 years of collaboration between the TEI of Crete and Oxford University, in trying to crack the Enigma of the Phaistos Code, the Holy Grail of Minoan Religion and hopefully to “Understand’ it as well.
Further information:
www.teicrete.gr/daidalika ‘From Linear B to the Phaistos Disk’ supported by the Pasiphae Research Lab of the TEI of Crete and TEDX talk 2014
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative condition caused by the damage of dopamine-producing neurons in a brain area known as substantia nigra (dopamine is an electrical signal mediator and helps movement control). Initially, PD affects mostly motor function but, in later stages, patients also suffer from mental-related symptoms. Medical drugs such as levodopa and dopamine agonists are typically used to control PD-related symptoms. In addition, physiotherapy is openly supported by a number of Parkinson clinical facilities and associations, as it helps in controlling and delaying PD-related symptoms.
Recent technological advances have made it possible to develop serious games in augmented or virtual reality settings with the aid of sensors such as Microsoft’s Kinect. Such games are meant to augment and not replace physiotherapy sessions and allow patients to exercise in front of a large TV monitor.
In this paper we discuss ways to enable customization in PD-oriented serious games using the example of “driving” an automobile on a road with alternating turns, straight paths, traffic lights, etc. The particular succession of these prefabs can be tailored by an attending physiotherapist to offer the intended rehabilitation opportunities to a given patient. This ability for parametrization is very important for PD, as it allows tailoring of a game to a patient not only in the first few establishing physiotherapy sessions, but also as medium-term gains from exercise or medication are realized or even as the disease progresses. For example, based on the particular motor dexterities of a given patient, the roadway can be dynamically generated based on past and current performance data. Finally, we discuss how to “map” PD specific physiotherapy exercises onto car controlling activities such as accelerating, breaking and turning.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a medical condition where the median nerve is compressed as it travels through the wrist’s carpal tunnel, causing pain, numbness and tingling in parts of the hand that receive sensation from the median nerve. Depending on the severity of the symptoms, treatment may include physiotherapy and/or surgery. Many patients resort to physiotherapy to reduce the pain and follow an exercise schedule for mobility and strength. Individualized therapy may add exercises to increase muscle strength in the hand, fingers and forearm – and in some cases, the trunk and postural back muscles – as well as stretching exercises to improve flexibility in the wrist, hand and fingers.
In this paper we discusses possibilities that technology-driven physiotherapy based on serious games can augment a more traditional physiotherapy exercise curriculum. Accordingly, we present a Unity3D-based game called RollerBall, the scenario of which combines CTS-specific physiotherapy exercises in a scenario aiming to guide a ball across a bridge in a 3D scene. In more detail, extensions/flexions and radial/ulnar deviations of the wrist are used to guide a ball over a continuously reconfigurable bridge without falling in the void below. The bridge is made of planks, some of which periodically move to form gaps and discontinuities. In addition, a number of moving obstacles must be avoided to make it to the other end of the bridge without being knocked out of it. The game employs the Leap Motion sensor, whose detailed wrist, hand and fingers tracking abilities make it a promising hardware platform for rehabilitation exercises tailored for patients suffering from CTS.
Claw hand is a condition in which the fingers are noticeably curved or bent. The main characteristic of claw hand is the hyperextension of MetaCarpoPhalangeal (MCP) joints along with flexion of Proximal InterPhalangeal (PIP) joints and Distal InterPhalangeal (DIP) joints. This condition can affect one or more fingers, on one or both hands. Depending on the severity of the condition, you may have difficulty using your hands to pick up and grasp items. In this work we present an exoskeleton splint for people that face the “Claw Hand” problem. The device consists of two parts, an exoskeleton glove for the damaged hand and an actuation unit that houses the necessary electronic circuits, a microcontroller, batteries and five RC-servo motors in order to drive the glove. The actuation unit is portable, lightweight with friendly interface and power autonomy. Finally experimental results are given to evaluate the practicability and effectiveness of the exoskeleton splint in grasping objects and mimicking human gestures.
Due to the increasing demand for embedded systems (ES) development and the shortage of qualified engineers in this field, there exists the need for establishing an efficient framework about the knowledge and skills provided by the higher educational institutions. Thus, by regarding the engineering education in ES at the Technological Educational Institute of Crete- Department of Electronic Engineering (TEIoC/DoEE), we evaluate the suitability of our educational framework, i.e. if the student learning outcomes fulfil industry needs, in both a qualitative and quantitative way. Taking into account the curriculum courses for the ES area offered to the students of TEIoC/DoEE as well as specific case studies of students who carried out their workplace learning (WPL) in an industrial environment, achievement of compliance between student learning outcomes and labor market needs, is examined. Based on survey results from questionnaires distributed to students, WPL industry and WPL academic supervisors, we, first, identify any relevant gaps. Furthermore, we provide suggestions for closing these gaps in terms of curriculum modifications.
The unique characteristics of the laser pulses as a processing tool in the field of high performance, solution processed and flexible bulk heterojunction organic solar cells (OSCs), as a case study in the research activities of the nanoelectronics & organic electronics research activities, are presented. The proposed techniques is strongly believed open new avenues towards the design and construction of the next generation OSCs.
WebRTC is a project that allows browser-to-browser voice, video and data communication without the use of plugins, offering a more immediate communication without the need of a centralized system. It enables rich, high quality RTC applications to be developed for the browser, mobile platforms, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and allows them all to communicate via a common set of protocols. By utilizing these technologies, WebRTC-enabled IoT devices could enhance the “telerobotic” and “telepresence” experience of their users, allowing them to not only “interact” with these “things” but also “see” the interaction taking place and even interact collaboratively.
In this paper we propose a communication protocol that allows calling and evaluating JavaScript functions and performing actions on remote peers. This protocol can be used in online collaboration platforms and by extension in IoT devices by using IoT JavaScript libraries such as Cylon.js. We also describe a language for exchanging collaboration information and metadata including whiteboard sketches and video annotations. We have developed an online collaboration platform that takes advantage of these technologies and protocols to offer peers the ability to collaborate in real time using whiteboards and text annotations on video streams which are generated from a variety of sources including web cams, screen captures and local video files.
DNA is considered to be the basis of life on earth. This is because nearly all of the genetic information in animals, plants and single cell organisms such as bacteria as well as most viruses is encoded as DNA sequences. The sequence of the human genome was discovered over the course of the Human Genome Project and was first revealed in 2003. It is over 3 billion base pairs long and 99.9% is shared between two humans.
This groundbreaking discovery eventually enabled the scientific
community to find coherences between diseases and genomic mutations. One prerequisite to these researches is to be able to obtain the sequence of a certain human, known as DNA sequencing. In 2014 a new method for DNA sequencing has become commercially available when the British company Oxford Nanopore Technologies introduced their MinION DNA sequencer. It is a small and portable device powered by a USB interface which enables the user to perform DNA sequencing almost anywhere anytime. Moreover it enables DNA analysis in real time through streaming data, immensely reducing the time to answer a biological question. As a consequence algorithms needed for DNA analysis require to be streaming aware and efficient enough to process the streamed data in the time they are generated.
This paper gives an overview of the DNA sequencing technologies available today and presents future scenarios. Furthermore approaches to a streamed data analysis are explained as an applied research in computational life sciences.
In this paper, we present a web-based framework for the interior decoration, which successfully merges Real-Time Communication, Web3D and Semantic Web technologies. The interior design concepts of the system are based on an OWL ontology which is hosted by Apache Jena Semantic Framework, while a SPARQL questionnaire with specific number of questions regarding to various parameters of the room space is filled by the users. The display of the appropriate decoration solutions was succeeded with the assistance of WebRTC protocol as the realtime communication mean and an X3DOM scene as the graphical layout according to their ontological descriptors. Moreover, the implemented GUI not only supports an automatic visual reconstruction of a design scheme in users’ browser, but it also allows them to modify the scene according to their desires. Also, we implement our own MCU server for multi-party video call, which is written in JavaScript language. Our approach enables WebRTC-based video and audio conferencing.
A key element in the field of bioinformatics is the alignment of two sequences. Alignment in this case means the comparison of the mentioned two sequences using a certain metric to evaluate the similarity of the sequences. A well known und still commonly used method is the Smith-Waterman-Algorithm, which is based upon a two step alignment procedure: Both sequences form the two axes of a n x m-matrix, where n and m are the respective sequence lengths. In the first step the matrix elements are calculated in an iterative fashion. In the second step, the so called back tracking the best alignment path within the matrix is being detected.
If one assumes the two sequences to be of the same length, the computational effort of the Smith-Waterman-Algorithm grows with O(n2). Hence, if e.g. the sequence length n=1024, more than one million matrix elements need to be calculated.
Therefore it would obviously be advantageous to look for methods, where the computational effort for the alignment can be significantly reduced, while at the same time the alignment quality is kept at the same or almost the same level. Since the optimal alignment path usually orientates rather close to the main diagonal of the matrix, the idea is to work with submatrices of length k < n.
A corresponding extension of the Smith-Waterman-Algorithm has been studied intensively. The results are being presented in this paper. Two versions with different arrangements of submatrices were studied. The first version arranges the submatrices along the main diagonal of the matrix while the second version orientates them along the respective maximum of the former submatrix.
To ensure no or only minimal loss in quality of an alignment, the dimensions for the submatrices and the overlap between two submatrices were researched with statistical methods. For all three versions of the algorithm the calculation times as well as the resulting alignments were compared.
For two sequences with the lengths of 1024 the number of calculated cells could be reduced from 1 million in the original algorithm to roughly one half in the versions with submatrices. This leads also to a reduced calculation time of about 50 %. The quality impact is 1 % at a length of 1024, but decreases significantly with growing lengths.
The so-called iBeacons have been introduced by Apple Inc. in 2013 in order to allow more precise location determination. This refers especially to indoor navigation (sometimes called micro-location or indoor-geo-location) where systems like GPS are not available. Originally developed for the iOS they are now also available for Android-based applications.
The technology is based on the Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) wireless protocol. As with all wireless devices the RF signal's intensity is used to determine contextual information, like location or proximity to other BLE devices. Position information is derived from the measured RSSI values (Received Signal Strength Indicator).
For many commercial applications a simple proximity indication employing single iBeacons has been sufficient. For more sophisticated applications (Internet of Things – IoT, Industry 4.0, home automation, etc.) a combination of several iBeacons can be used, typically extracting more precise location information through trilateration or triangulation.
In this paper we will discuss the possibility to use a method called “fingerprinting” for more precise position measurements. In this approach several beacons are distributed over the area in which locations have to be determined. In a first step a map of characteristic RSSI values is prepared, combining the signals produced by several transmitting beacons. Following this preparatory procedures, real-time applications are possible, measuring the RSSI-fingerprints and through comparison with the map determine the location.
The Android-based navigation system under development allows the use of standard BLE-compatible smartphones to do fingerprint navigation. We will present practical results and show under which conditions this method is advantageous compared to the simple proximity method.
Remote control of complex mechatronic systems, in an intuitive way, is not an easy task especially when we refer to robot manipulators and anthropomorphic robotic hands. In this case, teleoperation is often performed through expensive motion tracking systems along with uncomfortable data gloves in order to capture the configuration of the palm and the motion of the fingers.
For this reason we propose a teleoperation system that is solely based on optical data for controlling the motion of a robot hand with 22 degrees of freedom (d.o.f.). The proposed system does not require the user to wear any motion capture glove or other exoskeleton devices. The main task for the system is to imitate user’s hand configurations for grasping objects or doing human gestures. The system consists of the following subsystems: a) the 16 d.o.f. robotic hand “TALOS” that is developed by the Control Systems & Robotics Lab at the Technological Educational Institute of Crete b) the RV-2A six d.o.f. robot manipulator by Mitsubishi and c) the “3D Hand Tracking” software that is based on the RGB-D Kinect sensor and developed by the Computational Vision & Robotics Laboratory of the Institute of Computer Science /FORTH. The robot hand is used as a gripper at the end effector of the RV-2A robot manipulator. Finally we present experimental results that demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed telemanipulation system.
In an effort to address the ever increasing aircraft flying daily, a solution is sought in many areas of technology. So far, the most important roll plays Radar technology. On the other hand there is a continuous effort to reduce costs in every area of air navigation. Thus, the exact solution of the radar installation and maintenance is ready to give way to new, more efficient solutions. Such a solution could well be the use of high definition video recording cameras.
This paper presents a first part of a possible solution, that, of the recognition of the aircraft when it is on the ground. In order to identify an aircraft, it is sufficient to read the registration number printed on every single aircraft in the world and is unique, offering valuable information, in the same way the registration number of a car does. Because of the uniqueness of this coordinate data line, we can recognize the aircraft and also gather any other information we need in each case. Here it is used a simple camera and MATLAB software. The code applies to over 50 videos in real airport conditions and has high percentage success. Based on this, there is much room for growth and development of a low cost airport surface monitoring system (A-SMGCS) and why not for a remote aerodrome control tower (Remote tower).